Understanding the Nutritional Value of Sweet Potatoes
Key Antioxidants Found in Sweet Potatoes
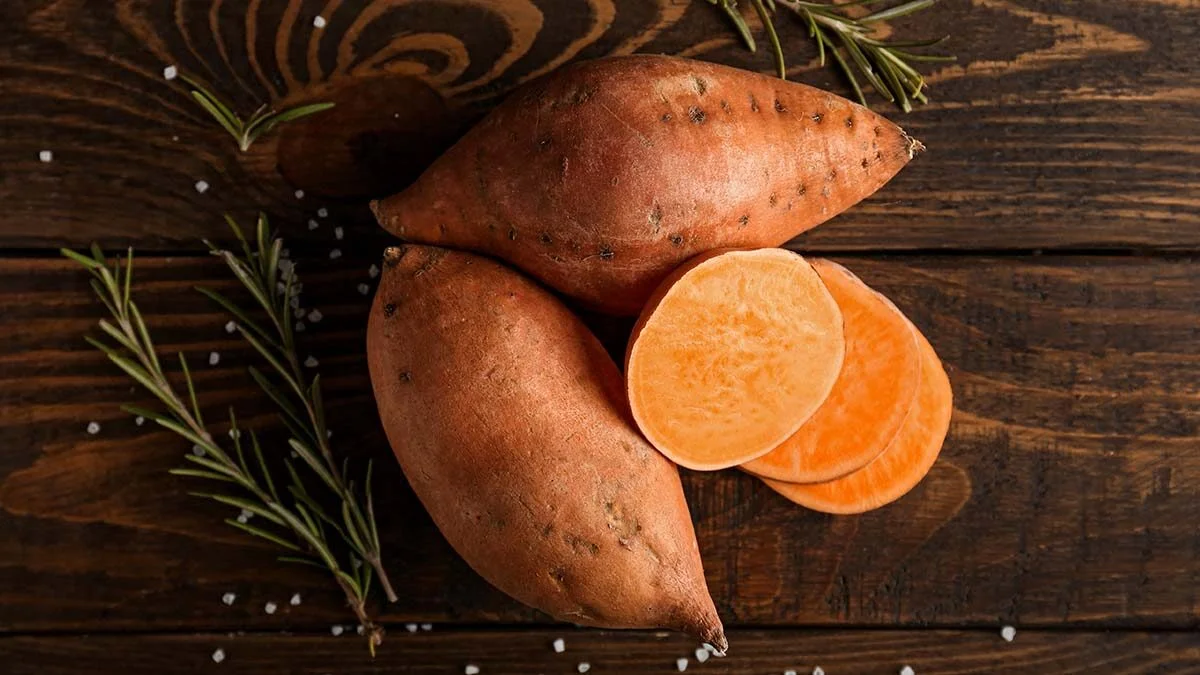
Sweet potatoes are rich in antioxidants, primarily beta carotene, along with Vitamins C and E. Beta carotene is a potent antioxidant contributing to the vibrant orange color of many sweet potato varieties. The skin also contains significantly higher antioxidant levels than the inner flesh, making it a valuable part of the vegetable.

Health Benefits Linked to Antioxidant Retention
Consuming sweet potatoes rich in antioxidants supports skin regeneration by promoting collagen production. Beta carotene protects eyes from oxidative stress, reducing risks of vision loss and improving night vision. Additionally, these antioxidants help protect lung tissues and maintain lung capacity, contributing to overall respiratory health.
Choosing the Best Sweet Potatoes for Maximum Antioxidants
Varietal Differences and Their Impact on Antioxidant Levels
Different sweet potato varieties vary in their antioxidant content. Orange-fleshed varieties typically offer higher beta carotene levels compared to white or purple types. Selecting the right variety ensures a better nutritional profile and greater health benefits.
What to Look for When Buying Sweet Potatoes
When selecting sweet potatoes, opt for firm tubers without soft spots or blemishes. Choose those with intact skin, as the skin contains concentrated antioxidants. Freshness is key; fresher potatoes retain more nutrients than those stored for extended periods.
Storage Tips That Help Maintain Antioxidant Content
Optimal Temperature and Humidity Conditions
Store sweet potatoes in a cool, dark, and well-ventilated place, ideally between 55-60°F (13-16°C). Avoid refrigeration, which can cause hardening of the center and negatively affect nutrient retention. Moderate humidity helps prevent shriveling while maintaining antioxidant levels.
Avoiding Common Storage Mistakes
Avoid exposure to light and plastic bags, which can trap moisture and encourage spoilage. Excess moisture or damp conditions promote decay, leading to nutrient loss. Proper airflow and dryness preserve the tubers’ antioxidant properties.
Preparation Methods to Preserve Antioxidants
Peeling vs. Leaving the Skin On
Keeping the skin on preserves antioxidants, as it contains nearly ten times more than the inner flesh. When cleaning sweet potatoes, gently scrub the skin instead of peeling it to maintain its nutritional benefits.
Cutting Techniques That Reduce Nutrient Loss
Chopping sweet potatoes into larger chunks minimizes surface area exposed to air, reducing oxidation and nutrient loss. Avoid finely dicing or shredding before cooking to better preserve antioxidants.
Cooking Techniques That Maximize Antioxidant Retention
Steaming and Boiling: Pros and Cons
Boiling skin-on sweet potatoes is one of the best methods to maintain beta carotene levels. It softens the tuber efficiently without causing excessive nutrient degradation. Steaming also retains nutrients but may be less effective than boiling for beta carotene preservation.
Baking and Roasting for Enhanced Flavors and Nutrients
Baking and roasting enhance natural flavors but can reduce antioxidant levels compared to boiling. High, dry heat may degrade some nutrients, so these methods should be used when flavor is the priority rather than maximum nutrient retention.
Avoiding Frying and Other High-Heat Methods
Frying exposes sweet potatoes to very high temperatures and oil, which can significantly diminish antioxidant content. Such methods also add unhealthy fats, making them less ideal for preserving beta carotene and other antioxidants.
Combining Sweet Potatoes With Other Foods for Better Absorption
Pairing with Healthy Fats
Beta carotene is fat-soluble, meaning its absorption improves in the presence of healthy fats. Drizzling cooked sweet potatoes with olive oil or another quality fat enhances the body’s ability to utilize these antioxidants effectively.
Spices and Herbs That Boost Antioxidant Effects
Adding spices like turmeric or cinnamon to mashed sweet potatoes can further elevate antioxidant intake. These spices contain compounds that work synergistically with sweet potato antioxidants to boost overall health benefits.
Summary: Best Practices for Selecting and Cooking Sweet Potatoes
To maximize antioxidant retention, choose firm, fresh sweet potatoes with intact skin, preferably orange-fleshed varieties. Store them in a cool, dry, well-ventilated place away from light. Prepare sweet potatoes by leaving the skin on and cutting into large chunks. Boiling skin-on sweet potatoes preserves the highest beta carotene levels. Enhance absorption by adding healthy fats like olive oil, and consider incorporating antioxidant-rich spices such as turmeric or cinnamon. Avoid high-heat cooking methods like frying to maintain the full nutritional profile.